Dynex
Compute on Dynex
Advanced Examples
Here are some advanced code examples and notebooks to be used to compute them on the Dynex neuromorphic computing platform:
RNA Folding
Finds the optimal stem configuration of the RNA sequence from the HIV virus and the Tobacco Mild Green Mosaic Virus using the Dynex platform. The example takes an RNA sequence and applies a quadratic model in pursuit of the optimal stem configuration.
Breast Cancer Prediction
This examples shows using the Dynex SDK Scikit package which provides a scikit-learn transformer for feature selection using the Dynex Neuromorphic Computing Platform. The number of features have impact on neural network training and accuracy. It will be demonstrated how a significant reduction of features lead to similar (or even better) results.
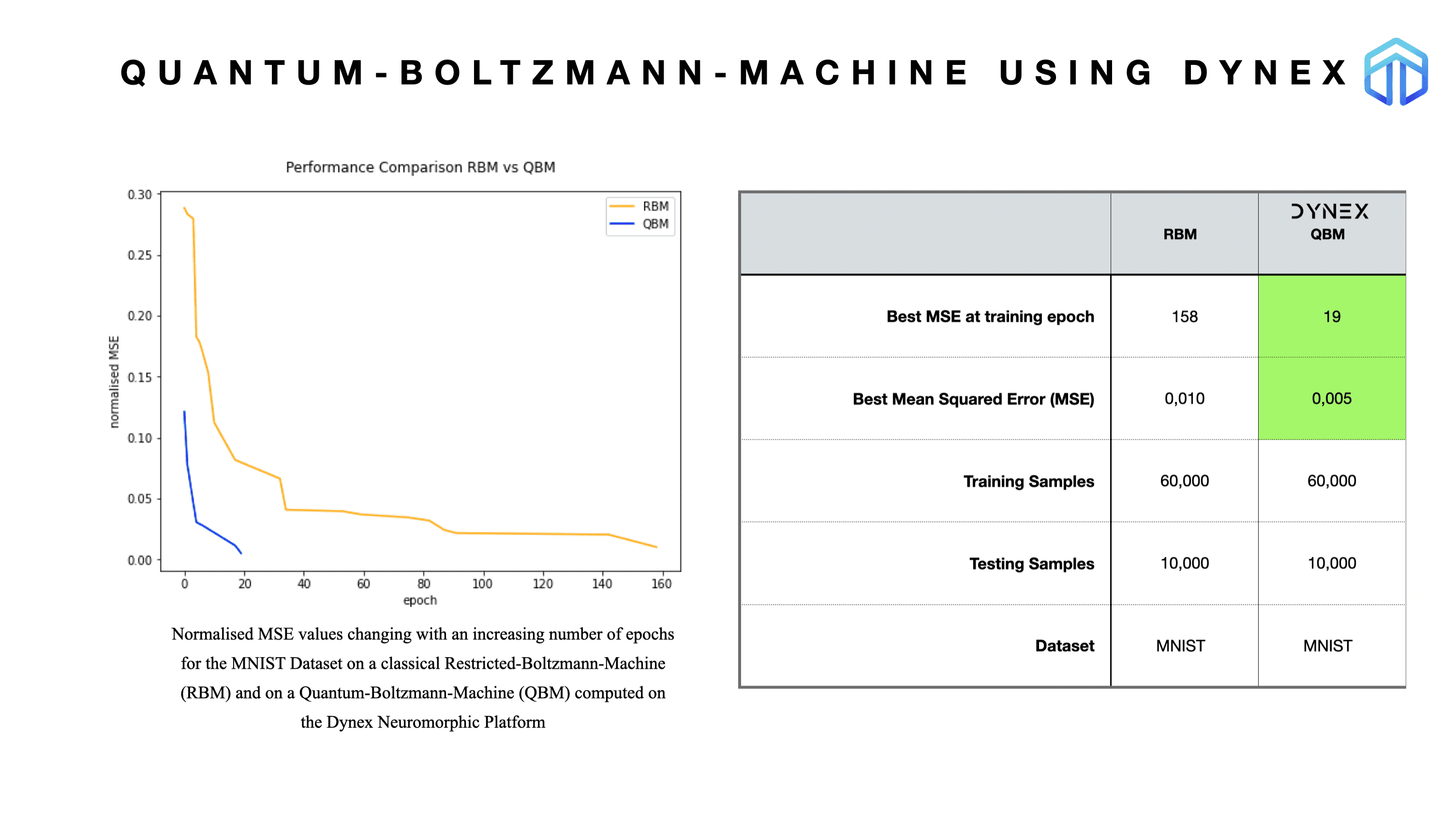
Quantum-Boltzmann-Machine (QBM) on the Dynex Platform
We demonstrate a Quantum-Boltzmann-Machine (QBM) implementation using the Dynex platform to perform the computations and compare it with a traditional Restricted-Boltzmann-Machine (RBM) applied on the MNIST dataset of handwritten digital images with 60,000 training and 10,000 testing samples.
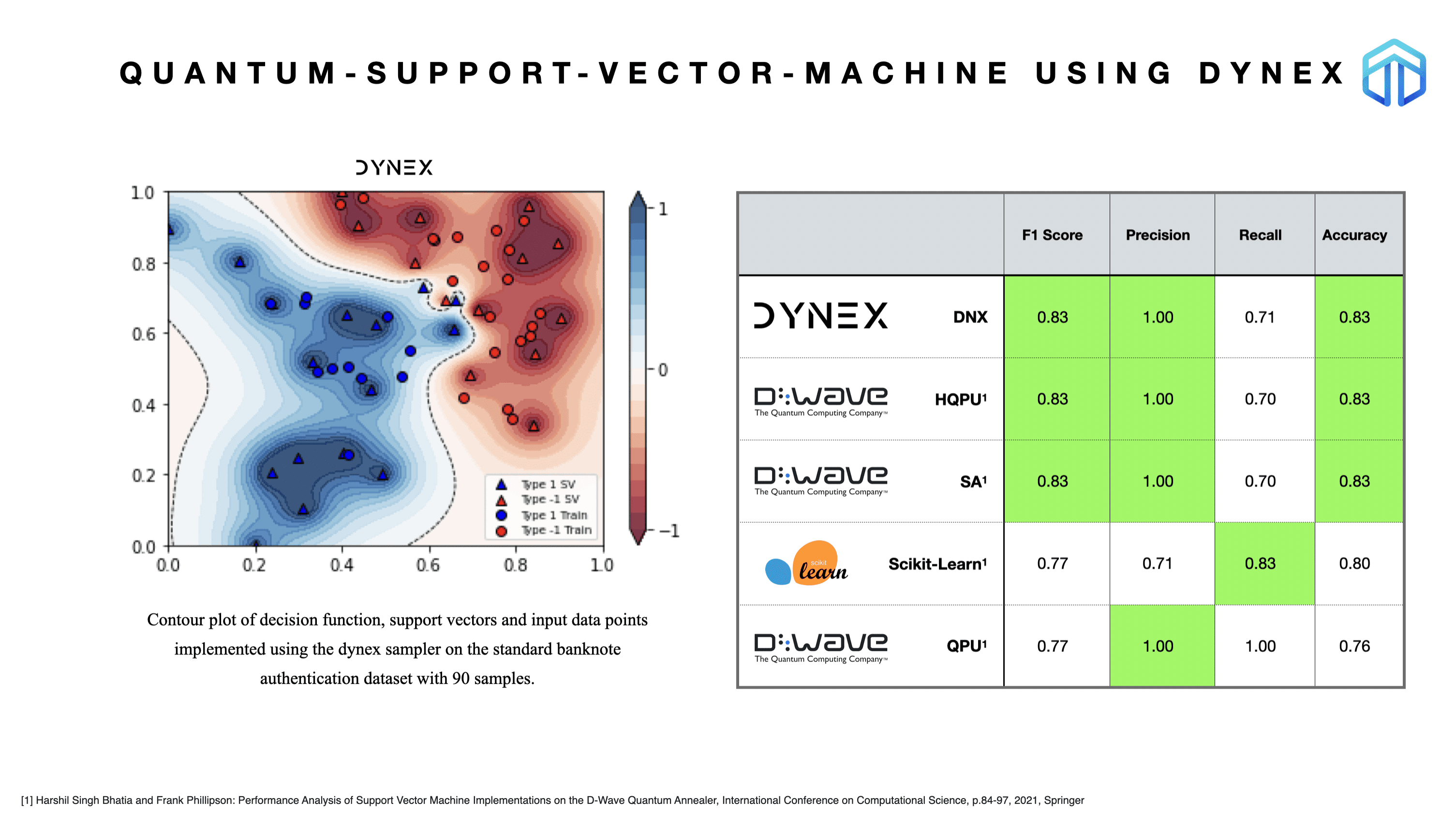
Quantum Support-Vector-Machine (QSVM) on the Dynex Platform
In this example a classical classification model, Kernel-Support Vector machine, is implemented as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimisation problem. Here, data points are classified by a separating hyperplane while maximizing the function margin. The problem is solved for a public Banknote Authentication dataset and the well- known Iris Dataset using the Dynex Neuromorphic Computing Platform.
Placement of EV Charging Stations
Determining optimal locations to build new electric vehicle charging stations is a complex optimization problem. Many factors should be taken into consideration, like existing charger locations, points of interest (POIs), quantity to build, etc. In this example, we take a look at how we might formulate this optimization problem and solve it using the Dynex Neuromorphic Platform.
Feature Selection
Feature selection for machine learning using mutual information to predict survivals of Titanic passengers. The method used is applicable to problems from a wide range of domains, for example financial portfolio optimization.
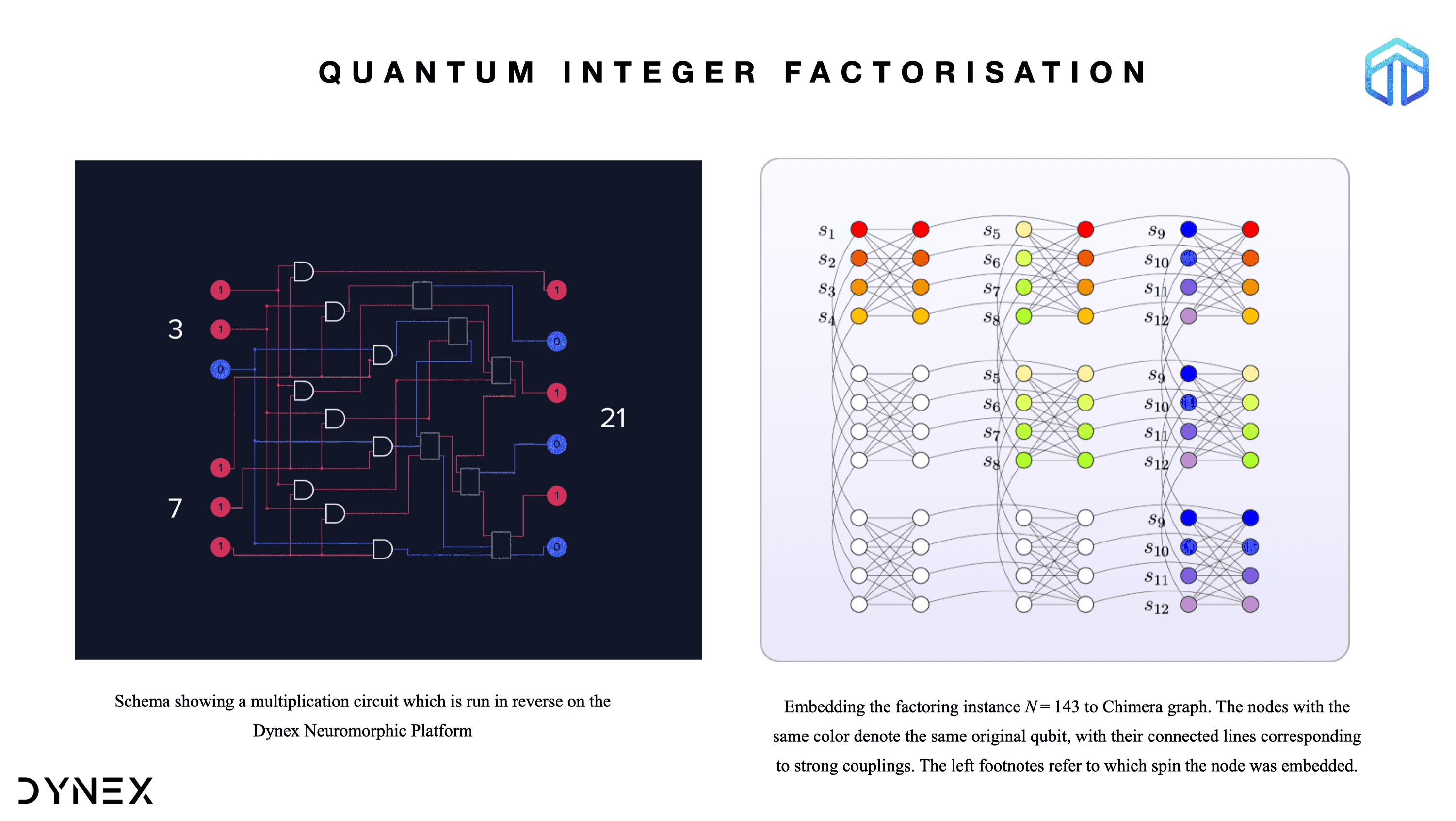
Quantum Integer Factorization on the Dynex Platform
Identifying new methods for integer factorization plays an important role in modern information security. Shor’s algorithm is perhaps the most well-known method for integer factorization. An equally powerful model of quantum computing is the adiabatic quantum computing (AQC) model, which can also solve the integer factorization problem. In this example, we show how to convert an arbitrary integer factorization problem to an executable Ising model and tested it on the Dynex Neuromorphic Platform.
Please note that our repositories are currently in development, you will find more and more sample code and tutorials in the near future.